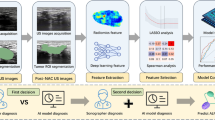
Abstract
Purpose
The automated segmentation of lymph nodes (LNs) in ultrasound images is challenging, largely because of speckle noise and echogenic hila. This paper proposes a fully automatic and accurate method for LN segmentation in ultrasound that overcomes these issues.
Methods
The proposed segmentation method integrates diffusion-based despeckling, U-Net convolutional neural networks and morphological operations. First, the speckle noise is suppressed and the lymph node edges are enhanced using Gabor-based anisotropic diffusion (GAD). Then, a modified U-Net model is used to segment the LNs excluding any echogenic hila. Finally, morphological operations are undertaken to segment the entire LNs by filling in any regions occupied by echogenic hila.
Results
A total of 531 lymph nodes from 526 patients were segmented using the proposed method. Its segmentation performance was evaluated in terms of its accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, Jaccard similarity and Dice coefficient, for which it achieved values of 0.934, 0.939, 0.937, 0.763 and 0.865, respectively.
Conclusion
The proposed method automatically and accurately segments LNs in ultrasound images, enhancing the prospects of being able to undertake artificial intelligence (AI)-based diagnosis of lymph node diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evans, K. D., Sammet, S., Ramos, Y., & Knopp, M. V. (2008). Image segmentation for evaluating axillary lymph nodes. Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography, 24(6), 329–336.
Zhang, Y., Ying, M. T., Yang, L., Ahuja, A. T., & Chen, D. Z. (2016, December). Coarse-to-fine stacked fully convolutional nets for lymph node segmentation in ultrasound images. In 2016 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM) (pp. 443-448). IEEE.
Pham, D. L., Xu, C., & Prince, J. L. (2000). A survey of current methods in medical image segmentation. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 2, 315–337.
Sarle, W. S. (2012). Algorithms for Clustering Data. Technometrics, 32(2), 227–229.
Zhang, K., Zhang, L., Song, H., et al. (2013). Reinitialization-free level set evolution via reaction diffusion. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 22(1), 258–271.
Zhang, Q., Song, S., Xiao, Y., et al. (2019). Dual-mode artificially-intelligent diagnosis of breast tumours in shear-wave elastography and B-mode ultrasound using deep polynomial networks. Medical Engineering & Physics, 64, 1–6.
McInerney, T., & Terzopoulos, D. (1996). Deformable models in medical image analysis: A survey. Medical Image Analysis, 1(2), 91–108.
Kuo, J., Mamou, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2017). Segmentation of 3-d high-frequency ultrasound images of human lymph nodes using graph cut with energy functional adapted to local intensity distribution. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 64(10), 1514–1525.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. International Conference on Learning Representations, 14(4), 1–14.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Hinton, G. E. (2017). ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM, 60(6), 84–90.
Gulshan, V., et al. (2016). Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA, 316(22), 2402.
Al-antari, M. A., Al-masni, M. A., Choi, M., Han, S., & Kim, T. (2018). A fully integrated computer-aided diagnosis system for digital X-ray mammograms via deep learning detection, segmentation, and classification. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 117(May), 44–54.
Dimauro, G., et al. (2019). Nasal cytology with deep learning techniques. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 122, 13–19.
Ciresan, D., Giusti, A., Gambardella, L., & Schmidhuber, J. (2012). Deep neural networks segment neuronal membranes in electron microscopy images. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 25, 2843–2851.
Avendi, M. R., Kheradvar, A., & Jafarkhani, H. (2016). A combined deep-learning and deformable-model approach to fully automatic segmentation of the left ventricle in cardiac MRI. Medical Image Analysis, 30, 108–119.
Cha, K. H., Hadjiiski, L. M., Samala, R. K., Chan, H.-P., Cohan, R. H., & Caoili, E. M. (2016). Comparison of bladder segmentation using deep-learning convolutional neural network with and without level sets. Medical Imaging: Computer-aided Diagnosis, 43(4), 97512.
Nida, N., Irtaza, A., Javed, A., Yousaf, M. H., & Mahmood, M. T. (2019). Melanoma lesion detection and segmentation using deep region based convolutional neural network and fuzzy C-means clustering. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 124, 37–48.
Shelhamer, E., Long, J., & Darrell, T. (2017). Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 39(4), 640–651.
Chen, L. C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., & Yuille, A. L. (2017). DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 40(4), 834–848.
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., & Jia, J. (2017). Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2881–2890).
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., & Cipolla, R. (2017). SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder–decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 39(12), 1–14.
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., & Brox, T. (2015). U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 9351, 234–241.
Yuan, Y., Chao, M., & Lo, Y. (2017). Automatic skin lesion segmentation using deep fully convolutional networks with jaccard distance. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 36(9), 1876–1886.
Alom, M. Z., Yakopcic, C., Taha, T. M., & Asari, V. K. (2018). Nuclei segmentation with recurrent residual convolutional neural networks based U-Net (R2U-Net). IEEE National Aerospace & Electronics Conference, 227(1–3), 327–333.
Perona, P., & Malik, J. (1990). Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 12(7), 629–639.
Zhang, Q., Han, H., Ji, C., Yu, J., Wang, Y., & Wang, W. (2014). Gabor-based anisotropic diffusion for speckle noise reduction in medical ultrasonography. Journal of the Optical Society of America. A, Optics, Image Science, and Vision, 31(6), 1273–1283.
Rosário, P. W. S., et al. (2005). Ultrasonographic differentiation between metastatic and benign lymph nodes in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine, 24(10), 1385–1389.
Evans, R. M., Ahuja, A., & Metreweli, C. (1993). The linear echogenic hilus in cervical lymphadenopathy—A sign of benignity or malignancy? Clinical Radiology, 47(4), 262–264.
Ying, M., Ahuja, A., Brook, F., & Metreweli, C. (2001). Vascularity and grey-scale sonographic features of normal cervical lymph nodes: Variations with nodal size. Clinical Radiology, 56(5), 416–419.
Dong, H., Yang, G., Liu, F., Mo, Y., & Guo, Y. (2017). Automatic brain tumor detection and segmentation using U-Net based fully convolutional networks. Med Image Underst Anal Conf, 723, 506–517.
Milletari, F., Navab, N., & Ahmadi, S. A. (2016, October). V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In 2016 fourth international conference on 3D vision (3DV) (pp. 565–571). IEEE.
Bottou, L. (2012). Stochastic gradient descent tricks. Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade, 7700, 421–436.
Kingma, D. P. & Ba, L. (2014). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980.
Simard, P. Y., Steinkraus, D., & Platt, J. C. (2003, August). Best practices for convolutional neural networks applied to visual document analysis. In Int Conf Doc Anal Rec, (vol. 3, pp. 958–963).
Supriyanto, E., & Zulkifli, N. (2011). Abnormal tissue detection of breast ultrasound image using combination of morphological technique. In WSEAS CSCC Multiconference, (pp. 234–239).
Kayalibay, B., Jensen, G., & van der Smagt, P. (2017). CNN-based segmentation of medical imaging data. Bioelectrochemistry, 75(2), 130–135.
Drozdzal, M., Vorontsov, E., Chartrand, G., Kadoury, S., & Pal, C. (2016). The importance of skip connections in biomedical image segmentation. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 10008, 179–187.
Tajbakhsh, N., et al. (2016). Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: Full training or fine tuning? IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 35(5), 1299–1312.
Acknowledgements
The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62071285 and 61911530249).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Wang, Y., Shi, J. et al. Segmentation of Lymph Nodes in Ultrasound Images Using U-Net Convolutional Neural Networks and Gabor-Based Anisotropic Diffusion. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 41, 942–952 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-021-00670-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-021-00670-8